Over 60% of newly planned mayonnaise manufacturing units end up delaying their launch by 3-6 months, not due to emulsion failure, but also because of incorrect layouts and gaps in compliance. Why are there so many failures after the installation of the plants? A mayonnaise factory plant like this one reveals the hidden factors that ultimately determine whether your initial production will be sold or discarded.
Month 0-1: Choosing the Right Market Before You Buy Anything
The first month has to be devoted to finding out what goods you will offer and who your customers are, even before considering machines or factory space. Your decision of what to sell with your mayonnaise-producing business is basically a domino that determines the whole subsequent chain of events.
Who Are You Selling To: Retail, HoReCa, or Private Label?
- Retail brands need long shelf life, attractive packaging, and room for distributor margins.
- HoReCa buyers are mostly interested in product consistency, bulk packs, and price stability.
- Private labels mainly focus on compliance, repeatability, and tight cost control.
Egg-Based vs Eggless Mayonnaise: Commercial Impact
- In India, mayonnaise without eggs is more widely accepted by the market. It makes the labeling very convenient for the vegetarian markets; however, it requires a bit more stabilizers.
- A mayonnaise with eggs has to be produced under very clean conditions, and the cold chain has to be maintained very strictly.
- The choice you make at this point will decide your emulsification process, shelf life, and the kind of equipment that you will require.
Also read: Egg-Free Mayonnaise – 5X Creamier & Healthy Delight
Month 1-2: Designing a Factory That Passes Inspection and Actually Works
Hygienic zoning prevents cross-contamination by separating areas based on risk, a critical step for egg-based products.
- Zone Separation: Differences in walls, pressure, and footbaths separate raw handling in Zone B from exposed product in Zone H.
- Personnel Controls: The microbial transfer from one zone to another is lowered by different uniforms, handwashing stations, and limited access per zone.
- India Compliance: Factories with FSSAI Schedule 4, which specifies the requirement for confirming zoning during audits, can operate without recall risks.
Space Integration: 500-2,000 sq ft facilities, plan 30% of the area for the High Zone with SS surfaces and HEPA filters.
Month 2–3: Equipment Selection Inside a Commercial Mayonnaise Plant Blueprint
In commercial mayonnaise factories, emulsification is achieved using very high shear colloid mills or rotor-stator homogenisers (e.g., 5,000-20,000 rpm) to produce oil droplets of <10 μm for stable emulsions.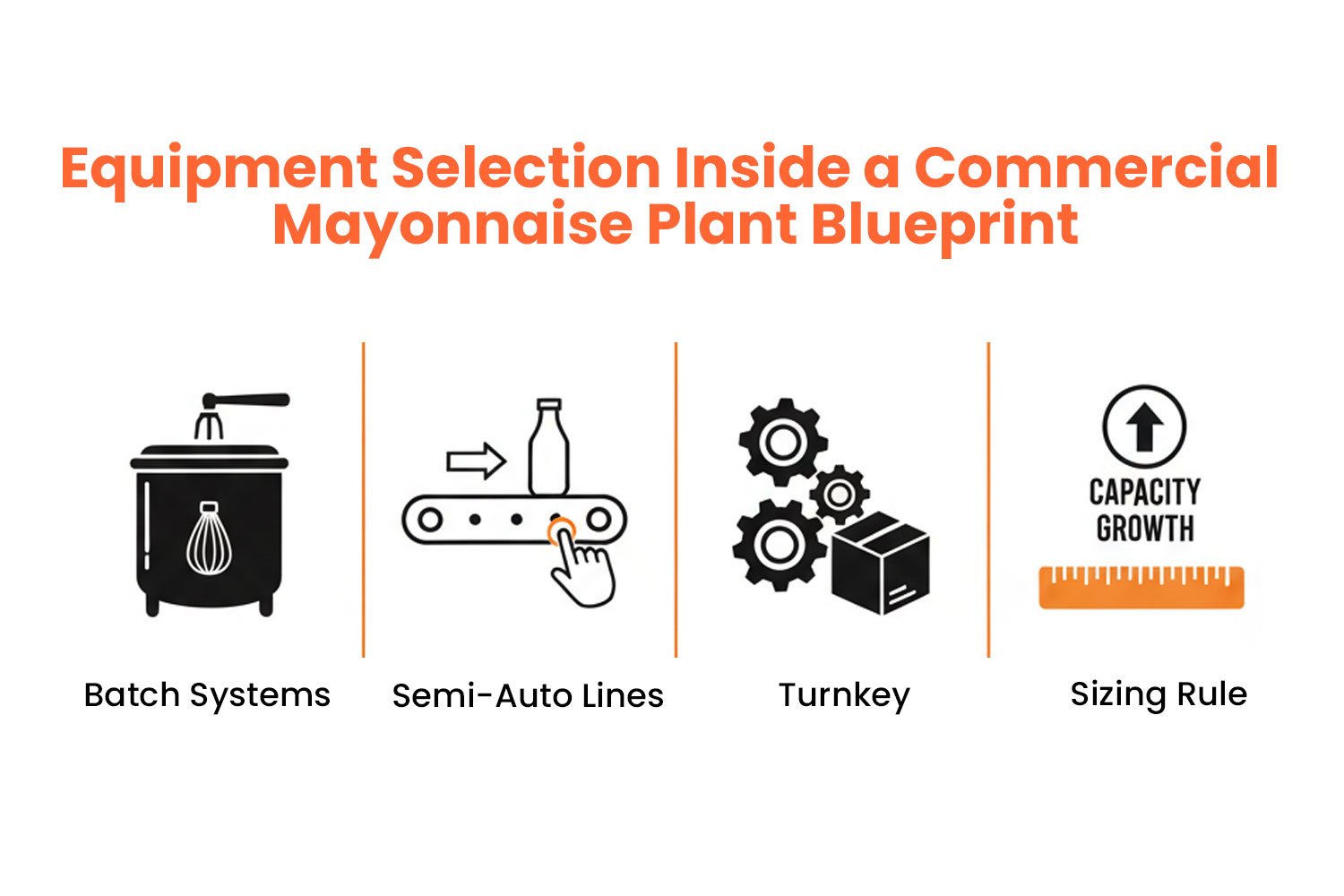
Equipment Selection Essentials
- Batch Systems: 100-300 kg/batch (e.g., jacketed vessels + inline homogenisers); startup-friendly, 24-hour cycles, 10-20L investment.
- Semi-Auto Lines: 500 kg/hr, uses metering pumps for accurate oil, water sequencing, labour drops by 40%, 300- 700 kg/day capacity is perfect for small manufacturers.
- Turnkey: Full automation (PLC-controlled, CIP-ready), 1,000 kg/day, 12 months payback via 95% yield.
- Sizing Rule: Figure out 70% capacity utilization as a baseline. For example, a 200L mixer for 500 kg/day will not be overloaded, ensuring stable operations.
Be in line with FSSAI-approved shear profiles to ensure a shelf life of more than 6 months.
Also read: Mayonnaise Production Equipment For Profitable Food Business
Month 3–4: Recipe Standardization & Shelf-Life Stability
Factory-scale mayonnaise recipes fail lab replication due to shear mismatch (lab is 10,000 rpm vs. production is 5,000 rpm), causing >20 μm oil droplets and creaming. Standardize via pH 3.8-4.2 (acetic/citric acid), 0.51% xanthan/gum arabic, and sequential addition are water, egg, and oil at 20–25°C.
- Standardization Pointers Process Validation: Rheometer should be utilized for viscosity 10, 000- 50, 000 cP to pilot three batches that will be used for matching lab texture.
- Stability Modifications: 75- 90 days ambient (PET bottles, < 30 °C), 180 days chilled by 0.1% EDTA, aw<0.92.
- Testing Protocol: The real-time shelf life is six months, and the accelerated shelf life is four weeks at 40°C and 75% RH. Microbial load <10 CFU/g is the product quality indicator that confirms product stability and lowers the risk of returns.
Month 4–5: Running Trial Batches and Locking Your Costs
Trial production demonstrates that 15-25% of the output is lost due to emulsifier shear gaps or overfilling, and these losses can be recuperated by 3-5 documented runs that monitor pH (3.8- 4.2), viscosity (20,000- 40,000 cP), and centrifuge oil recovery (>95%).
- Run Protocol: Record temp/shear changes, sensory panels rate texture (1-5 scale), yield 92-96%.
- Loss Benchmarks: Oil separation less than 3% is regarded as normal; if it is more than 5%, it indicates that the recipe needs to be changed.
- Full Costing Depreciation: ₹10/kg (20L machine/2yr), selling target 200/kg for 40% margin.
- FSSAI Tip: Ensure by lab (TPC <10^4 CFU/g) before opening the market.
Month 5–6: Preparing for Commercial Sales and Scale
Engage at least 3 anchor customers to gather real-world feedback on product consistency (viscosity ±5%), packaging seal integrity (leak <0.1%), and dispatch efficiency (24-hr TAT).FSSAI labels need to indicate allergens, nutrition (fat 70- 80%), and best before, confirmed by ASLT.
- Customer Focus: Pilot 500kg/, log feedback on texture/oil, off, iterate per-scale.
- Packaging: PET/HDPE jars (200g-1kg), induction, sealed test drop/heat (40 °C).
- Automation Trigger: Automate 1,000 kg/day, stable yield >94% if not, manual fills save 30% capex.
- Metrics: Target 40% margin (200/kg sell), monitor OTIF >95%.
Also read: Mayonnaise Machine Supplier Vs Turnkey: The Real Difference
Why Most New Mayonnaise Plants Struggle in the First Year
Mayonnaise factories lose 60% of their potential within the first year. Many failures happen because machines are purchased before finalizing the recipe, locking incorrect shear rate, for example, a 3,000rpm mixer instead of the required 15,000rpm can cause 20% oil separation. Poor layout may lead to FSSAI zoning issues, cross-contamination, and Salmonella risk (>10 CFU/g); the pilot masks 15-25% yield gaps from temperature changes (25±2°C critical).
- Fatal Mistakes & Fixes Machine Pre Buy: Finalize the recipe first; test the shear via a rheometer for <5m droplets.
- Emulsification Blindness: Sequence water, egg, oil at pH 4.0; disregard texture collapse.
- Layout Lapses: Implement 3, zone barriers, and positive pressure in high-risk areas; perform the audit pre-launch.
- Trial Skip: Conduct 5 pilots logging viscosity/yield; stabilizes 94%+ output.
- Premature Scale: Reach 500kg/day of consistency before 1,000 kg; otherwise, 30% rework.
Conclusion
The mayonnaise plant blueprint is essential for steering clear of a costly mistake in the early stages. We at Foodsure Machines are the ones who bring, engineer, and encourage the creation of facilities with which you can simply and rapidly move to the next level. We realise that it is a definite method for your first industrial batches to be successful, not difficult.