Did you know that over 60% of commercial mayonnaise batches fail in texture or stability after lab trials? Why does a perfect recipe often flop at scale? The secret isn’t just ingredients, it’s precise mayonnaise formulation R&D and mayonnaise quality control parameters. This guide shows exactly how to get 5-star consistency every time.
Why Most Mayonnaise Fails After Scale-Up | Mayonnaise Formulation R&D Issues
If your mayonnaise was flawless in the pilot batches yet didn’t turn out well in production, you’re not alone.
Typical problems after scaling up a production process might be:
- Oil separation within a few days or weeks.
- The product looks quite shiny, but a very weak structure.
- Inconsistency from one batch to another.
- Decreased shelf life.
- High rework and raw material loss.
These issues are not the result of a wrong recipe. They arise because the most important quality parameters for mayonnaise control are not maintained in the manufacturing scale.
The 6 Core Mayonnaise Manufacturing Parameters That Decide Final Quality
Industry insight breaks down the 6 core factors of industrial mayonnaise production, which came from real-world emulsification challenges in a high-volume plant (e.g., 5- 10 ton batches). Missing these results in yield loss of 10%- 20% or product recalls.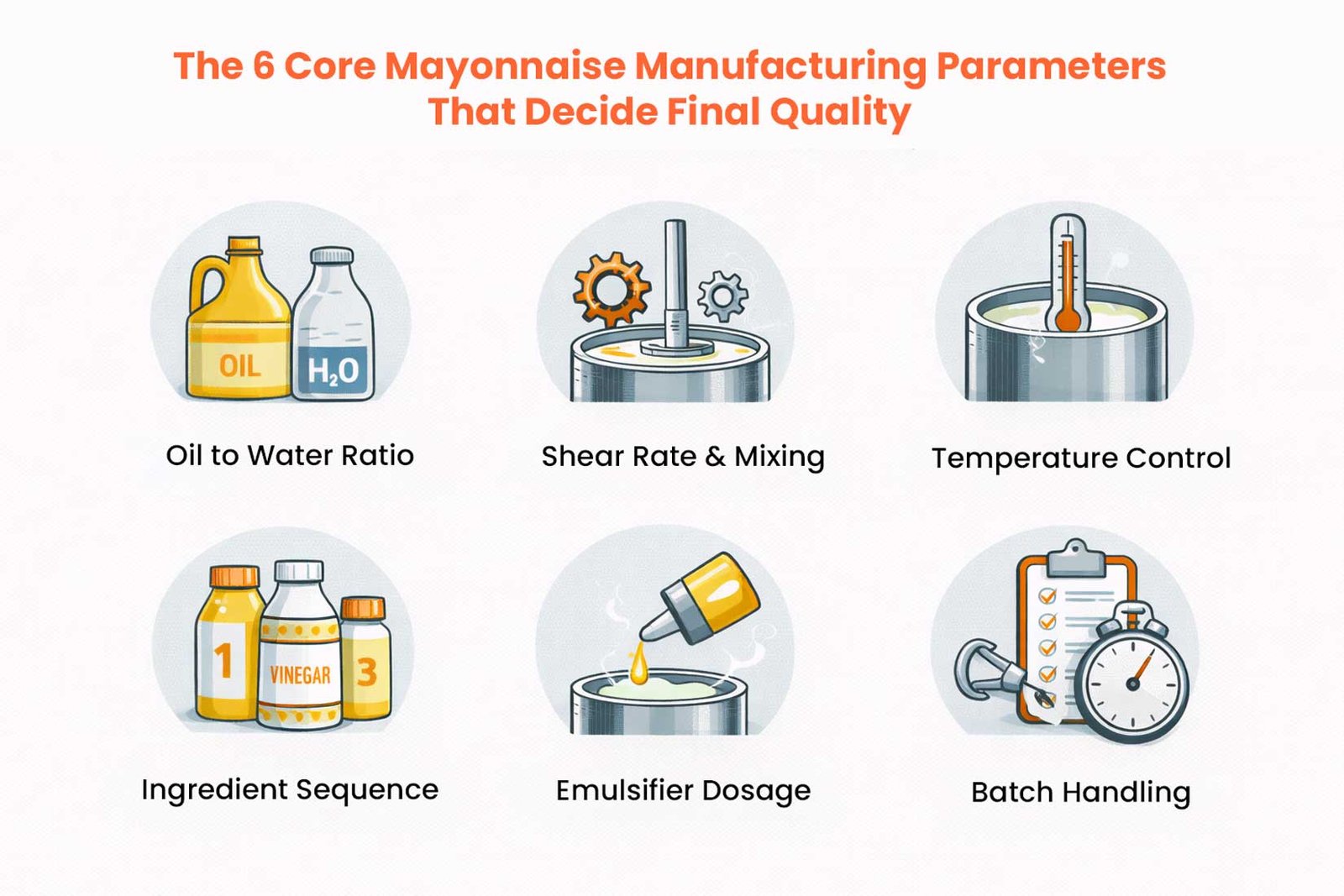
- Oil-to-Water Ratio: Target 70 – 80% oil, 1% deviation causes creaming (droplet size >10 μm). For immediate O/W control, inline refractometers should be used along with 1- 2% egg yolk or modified starch as the emulsifier.
- Shear Rate & Mixing: 10,000- 20,000s⁻¹ through colloid mills, an inconsistent shear result yields D >5µm, causing separation. To avoid over-shear coalescence, you should balance it with RPM staging.
- Temperature Control: 20- 30°C is the ideal temperature for lecithin to be activated. At over 40 °C, proteins are denatured the zeta potential drops below 30mV. Viscosity changes are avoided by PID loops.
- Ingredient Sequence: Hydrate gums first (xanthan/guar 0.2 – 0.5%), then acidify after 50% oil, at <1 L/min. Scale reversals result in gelation failures.
- Emulsifier Dosage: 1- 3% very accurately via mass flow meters; an overdose of emulsifier causes the product to become bitter (off-flavor volatiles), while an underdosing reduces the shelf life to less than 6 months.
- Batch Handling: Holding for less than 30 minutes at agitation of less than 10 rpm, peristaltic pumps are used to minimize shear (<5000 s). Yields hit 98% with scraped-surface transfers.
Also read: Top Industrial & Small-Scale Mayonnaise Machines: 7 Best Picks
R&D vs Manufacturing in Mayonnaise Production | Common Quality Control Mistakes
R&D vs Manufacturing in Mayonnaise Production uncovers significant differences are Lab trials (1-5kg) involve manual whisking at 500 – 1,000 s shear, resulting in D <2m droplets by visual checks, but do not consider scale-up physics. Production (5 – 10T batches) has 15,000s colloid mill shear, operator variances (5% dosing), and 2 4-hr hold times that decrease zeta potential from 45mV to 25mV, thus creaming rates are increased 3 times.
Common QC Mistakes:
- Scaling recipes linearly (fails to take into account changes in Reynolds number, causing a 20% yield loss).
- Not conducting pilot (50, 500kg) validation emulsions break at 70% oil load.
- Operators overriding PID temps (>35C causing emulsifiers to denature.
- No inline NIR for real-time O/W ratios resulting in off-spec batches.
- Reconnect through CFD modelling and inline particle analysers to achieve 95%+ transferab
How Industrial Mayonnaise Machines Maintain Quality & Stability
Mayonnaise making machine (e.g., 5 – 10T/hr continuous lines) maintain their stability through very precise engineering, thus they are able to achieve around 98% yields vs. 80% in batch systems.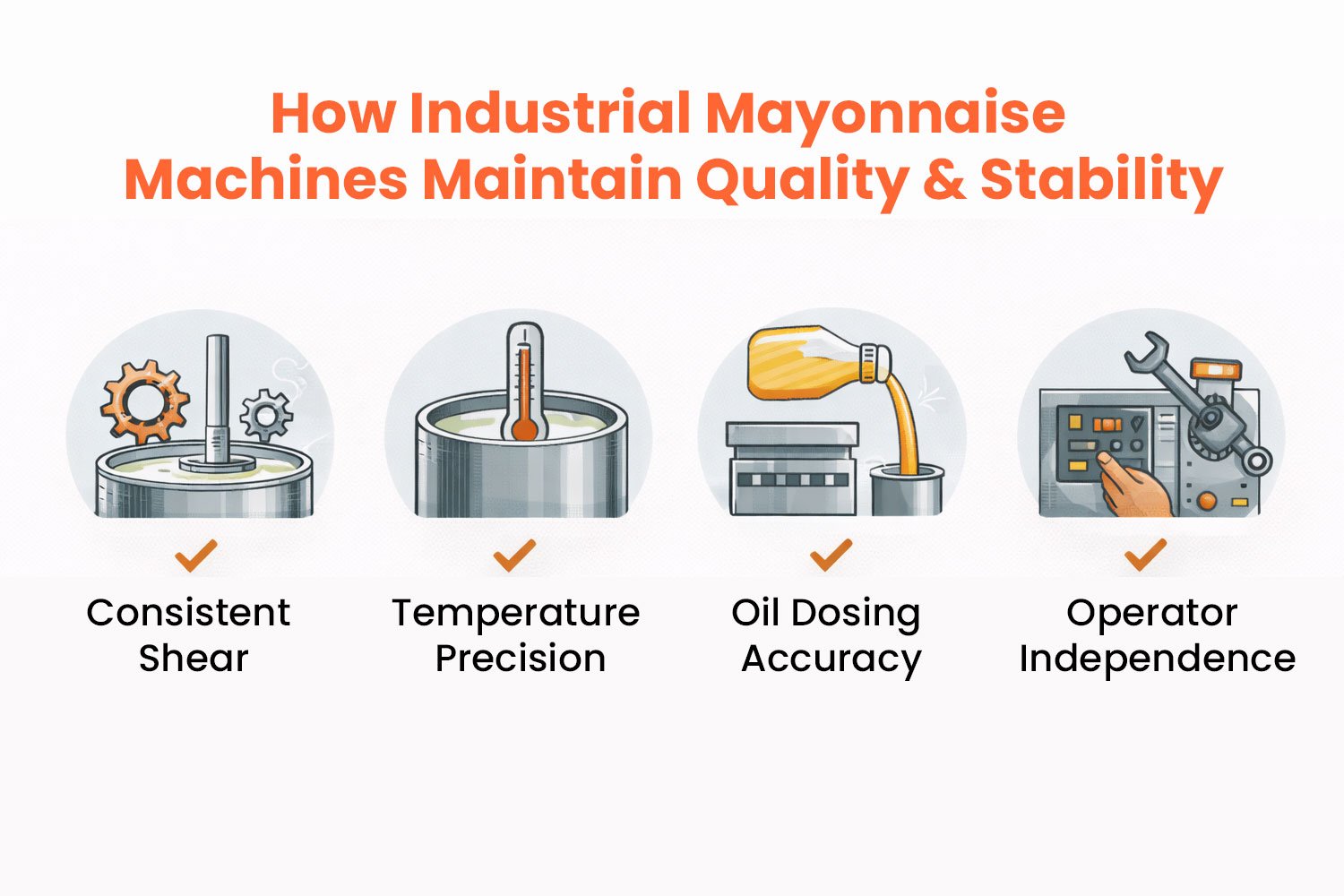
Consistent Shear: Inline colloid mills deliver 15,000- 25,000 s at fixed gaps (0.1-0.3mm), thus they can maintain D <3m droplet, VFD motors auto-adjust RPM to prevent over-shear coalescence.
Temperature Precision: Jacketed PID, controlled vessels maintain 22 – 28 °C (0.5C °C), thus they can preserve zeta potential > 35mV, heat exchangers recover 90% energy.
Oil Dosing Accuracy: Coriolis mass flow meters (0.1% error) are the ones that sync 70- 82% oil with water, thus real-time NIR feedback is able to avert phase splits.
Operator Independence: PLC/SCADA automation with recipe locking is the factor that leads to cutting variances by 70% auto CIP is the one that helps in downtimes, slashing to <2hr/shift. Yields increase by 15- 20%, shelf life reaches 12+ months, and rejections are reduced to less than 1%.
Also read: Mayonnaise Machine Price India: 2026 Cost Guide & ROI
Conclusion
At Foodsure Machines, we are convinced that an excellent mayonnaise is the result of a carefully developed mayonnaise formulation R&D and not by chance. We support producers to integrate essential parameters into their operations in such a way that the quality can be maintained at a large scale. The process becomes flawless when we are the engineers of it; our partners widen their business without having to worry about rework.
Frequently Asked Questions – Mayonnaise Formulation R&D
What is mayonnaise formulation R&D?
It’s the work of building recipes and process conditions that still hold up when production scales.
Why does mayonnaise fail after scale-up?
Lab formulations rarely match the shear, mixing, and stress of real production.
What causes oil separation in mayonnaise?
It usually comes down to weak emulsifier activation, poor shear control, or an unstable oil balance.
Which emulsifier works best for industrial mayonnaise?
It depends on oil load, shear intensity, and how the overall process is designed.
How important is shear in mayonnaise formulation R&D?
Shear controls droplet size, and droplet size decides texture, stability, and shelf life.
What temperature is ideal during emulsification?
Most processes work best around 18–25°C, where emulsifiers stay effective without damage.
Can a lab recipe work in commercial production?
Yes, but only after it’s rechecked against industrial equipment and real batch volumes.
How does ingredient addition order affect mayonnaise quality?
Get the order wrong, and the emulsion weakens before it has a chance to stabilize.
Why is batch-to-batch consistency so hard to maintain?
Manual control and loosely defined parameters introduce variation every single run.
How is shelf life improved during formulation R&D?
By tightening control over droplet size, pH, emulsifier dosage, and plant hygiene.
What role do machines play in mayonnaise formulation R&D?
They hold critical parameters steady so results don’t depend on operator judgment.
When should manufacturers revisit mayonnaise formulation R&D?
Any time they scale up, switch ingredients, or start seeing quality complaints.